
line
Healthy eyes are our top priorityline
Hangil Eye Hospital Comprehensive Eye Health Examination
Step 01
Visual inspection
Uncorrected vision ist the original vision not wearing glasses or lens. Best corrected visual acuity is the maximum refractive vision that are corrected. Uncorrected visual acuity of 0.6 or less usually need to wear glasses.

Step 02
Manifest refraction test
The Refractometry can check the cause of abnormal refractive errors of the eye. This test use a plane reflector in a dark room.
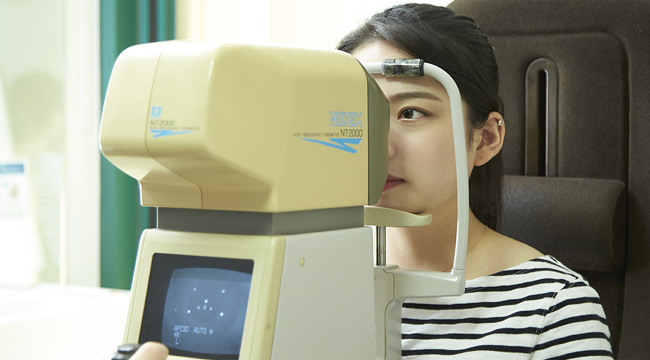
Step 03
IOP inspection
The intraocular pressure is the pressure of the liquid that filled with water in the eye. Our eyes are always created in a certain amount of water and also circulated.
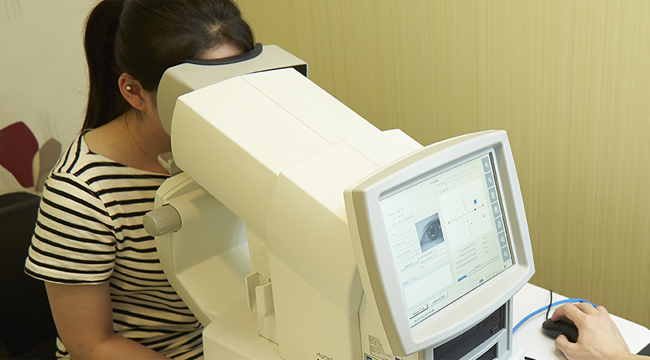
Step 04
Refractive
This test is to know for the refractive errors such as nearsightedness (myopia), farsightedness (hyperopia), and astigmatism.

Step 05
CCT Scan
This test measures corneal thickness to determine the value of the tension, and to diagonose the disease, such as keratoconus and inflated thinning corneal.

Step 06
Corneal Topography
It measures the anterior and posterior surface of the cornea, its curvature and shape also. It is used to diagnose keratoconus and other corneal diseases.

Step 07
OQAS Test
This test measures objective quality of vision through the degree of light scattering. It is possible to diagnosis from a variety of pathological cause.
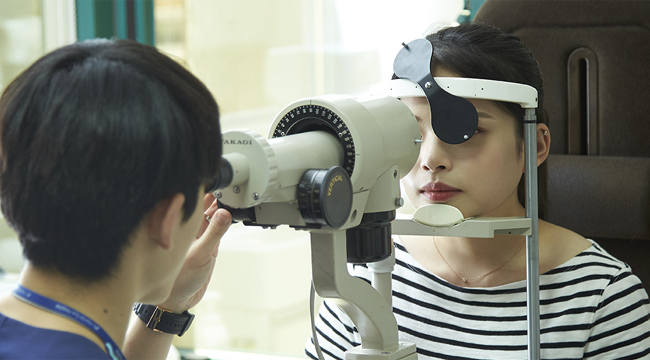
Step 08
Color vision test
The color vision is the ability to distinguish and recognize a color of an object according to the wavelength of its visible ray. It is a function of the cone cells of the retina. All of the color that a normal person feels are expressed with mixture of colors by monochromatic colors(red, green, blue). The incomplete three colors(red, green, blue) of the cone cells are diagnosed by color weakness or colorblind.
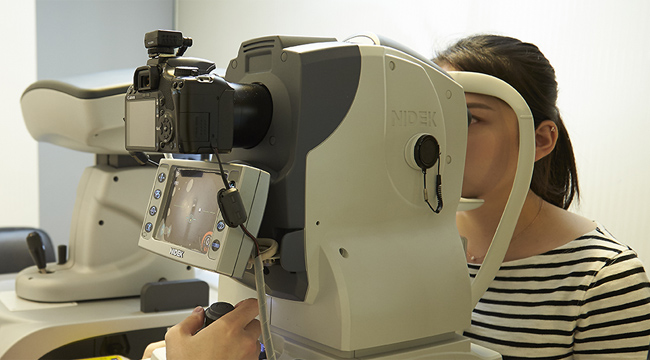
Step 09
Fundus photography(F-Photo)
Fundus is located in the innermost part of the eye. This inspection takes the inside of the eye's optic nerve and retina with digital photograph. It is used to determine the overall status of ocular disease and to compare the progress of the materials.
Step 10
FDTP
(Frequency Doubling Technology Perimeter)
This vision test can measure how much the eye can see and diagnose a variety of visual dysfunction such as retina or optic nerve dysfunction, glaucoma and other eye diseases.

Step 11
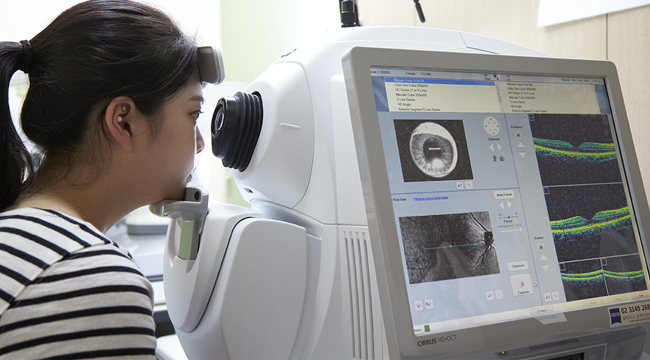
OCT
(Optical Coherence Tomography) Examination
This test can observe and measure the fine structure of the each retina floor including the optic nerve through the OCT. It is easy to understand if you think a CT scan for a comprehensive eye examination.

Step 12
Strabismus test
It measures the degree of the ocular deviation,type(heterot ropia, heterophoria, intermittent, homeostasis, etc.), and form(horizontal, vertical).

Step 13
Slit lamp examination
This test is the most basic ophthalmic examination to consider the presence of the disease of the front eye part like conjunctiva, cornea, lens.

Step 14
BUT
(Tear film break-up time measurement tests)
This inspection measures the time of the dried tear film with the slit lamp after staining conjunctival and flashes.

Step 15
Precision fundus examination
After putting the eye drops to wide pupil of the eye, it can look at the state the center and the periphery of the retina, retinal vessels and optic nerve, by using a special mechanism such as directly above ophthalmoscope, indirect ophthalmoscope, 3mirror optic nerve microscope.

Step 16
Overall diagnosis
Our excellent eye specialists evaluate detailed inspection results and make a diagnosis on the basis of enough consultation with a patient.
이전
다음